Contra Account Nature, Purpose & Examples
Posted in Bookkeeping

The purpose of the Accumulated Depreciation account is to track the reduction in the value of the asset while preserving the historical cost of the asset. Examples of deferred unearned revenue include prepaid subscriptions, rent, insurance or professional service fees. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting.
Accounts Payable Meaning, Examples and Accounting Definition
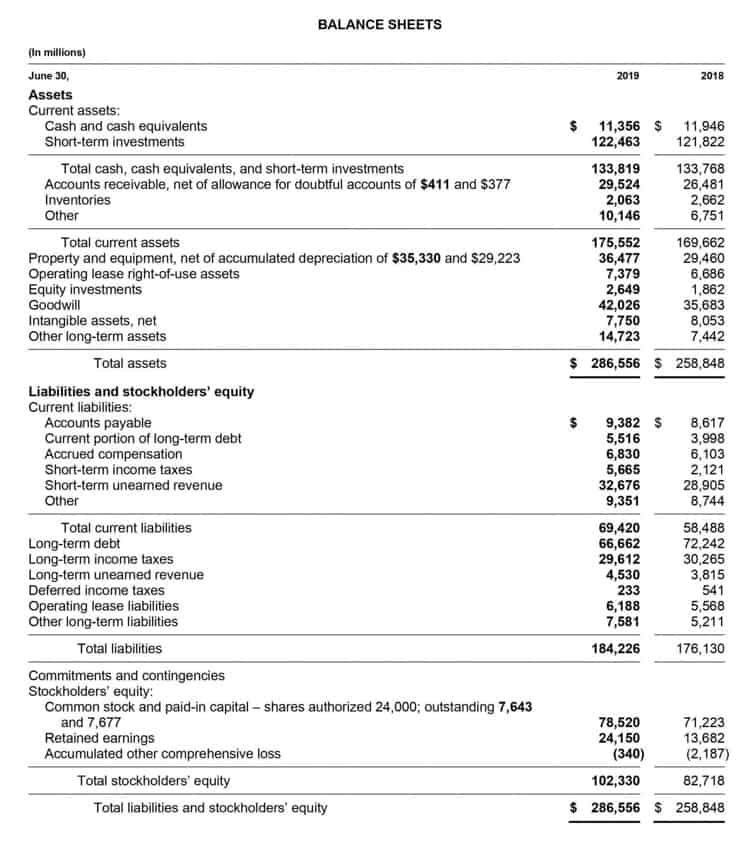
A contra revenue represents any deductions or offsets that need to be removed from gross revenue to provide a clearer understanding of actual income — such as in the example just provided. These accounts will typically help track sales discounts, product returns, and allowances (e.g., a price reduction for a good with minor defects). Some of the most common contra assets include accumulated depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, and reserve for obsolete inventory.
- Instead, you need to record this value gap, and a contra asset account serves that purpose.
- When considering all of the money currently owed to your business that’s recorded in your Accounts Receivable (A/R) line item as an existing asset, there’s a good chance that not all of those customers are going to pay you back in full.
- Contra liability, equity, and revenue accounts have natural debit balances.
- To obtain a cash payout before the note reaches maturity, you can sell these notes to a bank or other financial institution for some price below the note’s face value.
- For example net sales is gross sales minus the sales returns, the sales allowances, and the sales discounts.
- The company’s income statement will report the combination of the amounts in accounts 4210 and 4211 in order to show the company’s actual expense of $8,000 ($10,000 minus $2,000).
Is Unearned Revenue a Contra Account?
- Contra equity is a general ledger account with a debit balance that reduces the normal credit balance of a standard equity account to present the net value of equity in a company’s financial statements.
- It is not classified as a liability since it does not represent a future obligation.
- Note that accountants use contra accounts rather than reduce the value of the original account directly to keep financial accounting records clean.
- Contra accounts are confusing at first, but, with a little study, understanding them becomes second nature.
- Let’s go over how they work and what the main types are, and then finish with an example.
- Inventory obsolescence is an expense account, while the allowance for obsolete inventory is a contra asset account, which aims to reduce the inventory valuation on your balance sheet.
- Home Depot reports that returns are estimated at the time of the sale based on historic returns numbers.
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. If you keep a lot of inventory in stock, chances are that some of the inventory will become obsolete. This frequently happens to manufacturing companies that sell products with an expiration date since any inventory remaining in stock past the expiration date quickly becomes obsolete.
Contra Revenue Account

The accumulated depreciation account appears on the balance sheet and reduces the gross amount of fixed assets. Key examples of contra asset accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts and accumulated depreciation. Accumulated depreciation reflects the reduction in value of a fixed contra expense account asset. The sales discounts contra revenue account records the discounts given to customers on sales made to them, normally a cash or settlement discount. The account is normally a debit balance and in use is offset against the revenue account which is normally a credit balance.
- CCC estimates that 5% of accounts receivable will most likely be unrecoverable.
- When the account receivable is written off, it is added to bad debt expense on the income statement and placed in the contra account.
- In order to keep the accounts receivables as clean as possible with their historical values, we will use this contra account called allowance for doubtful accounts.
- There are four key types of contra accounts—contra asset, contra liability, contra equity, and contra revenue.
What is a Contra Revenue Account?
- The following are examples of commonly-used contra asset accounts you could create to better understand your business financials.
- For industries that rely on natural resources — mining, logging, oil, gas — depletion tracks the gradual exhaustion of the raw material in question, offsetting that loss in value against the initial appraisal of the land.
- When the two balances are offset against each other they show the net balance of both accounts.
- GAAP, the allowance for doubtful accounts represents management’s estimate of the percentage of “uncollectible” accounts receivable (i.e. the credit purchases from customers that are not expected to be paid).
- Wanting to spruce up its aging inventory, Show-Fleur purchased new, climate controlled-seats for its fleet, delivering increased comfort for passengers and a cleaner, more modern look for vehicle interiors.
GAAP, the allowance for doubtful accounts represents management’s estimate of the percentage of “uncollectible” accounts receivable (i.e. the credit purchases from customers that are not expected to be paid). The net amount – i.e. the difference between the account balance post-adjustment of the contra account balance – represents the book value shown on the balance sheet. The allowance method of accounting allows a company to estimate what amount is reasonable to book into the contra account.

How to Calculate Units of Activity or Units of Production Depreciation
Contra revenue




